

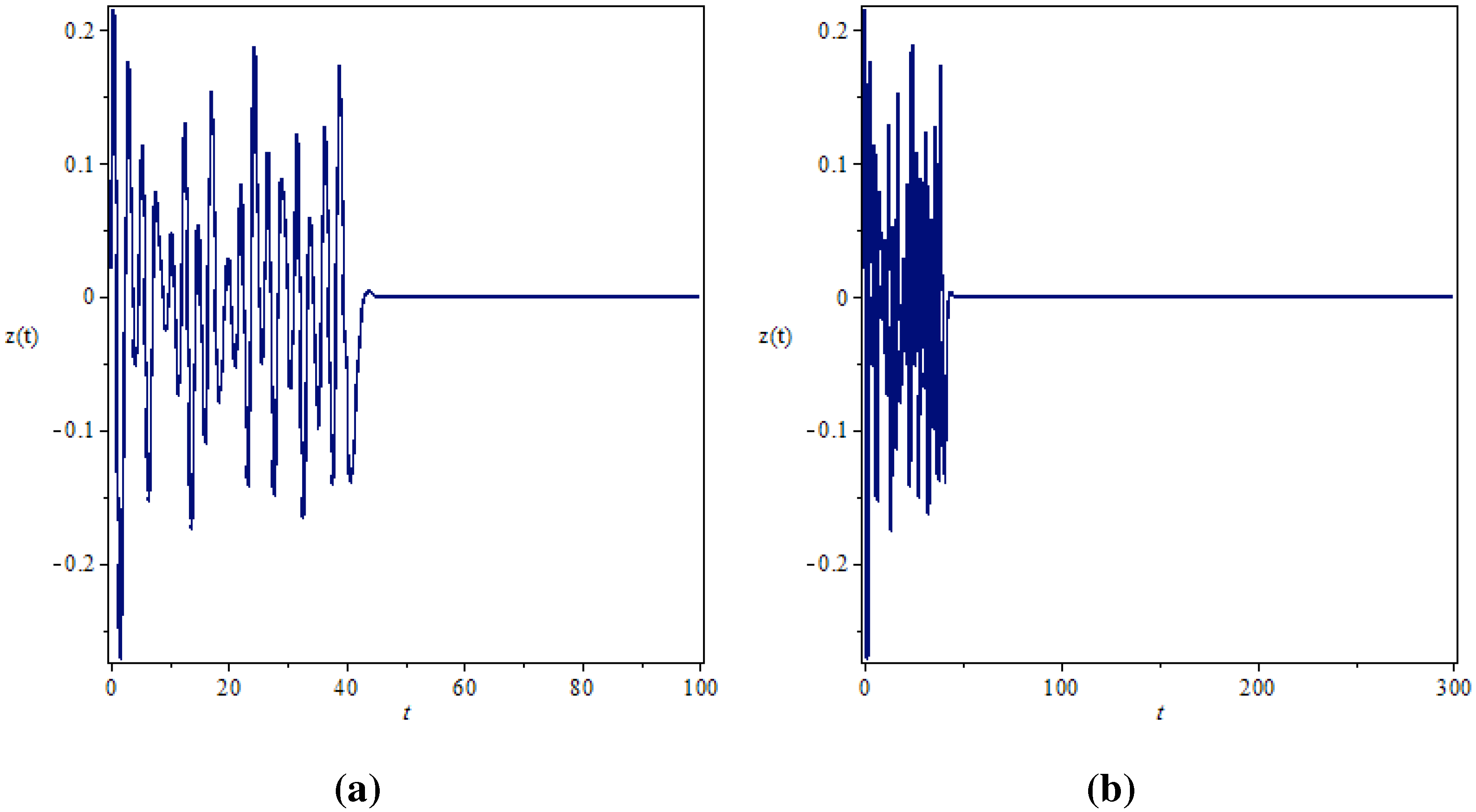
Therefore, the way you compute distances between the objects will play a crucial role in the classifier algorithm’s performance. Additionally, choosing a distance metric would have a strong influence on the performance of the classifier.

dissimilarity) is meant to be a metric if and only if it satisfies the following four conditions:ġ- Non-negativity: d(p, q) ≥ 0, for any two distinct observations p and q.Ģ- Symmetry: d(p, q) = d(q, p) for all p and q.ģ- Triangle Inequality: d(p, q) ≤ d(p, r) + d(r, q) for all p, q, r.ĭistance measures are the fundamental principle for classification, like the k-nearest neighbor’s classifier algorithm, which measures the dissimilarity between given data samples. Therefore, the smaller the distance is, the larger the similarity will get.Ī given distance(e.g. In other terms, A and B have a strong correlation. Thus, the similarity between A and B is higher than A and C or B and C. As you can tell, A and B are close enough to each other in contrast to C. Each data sample can have a single value on one axis(because we only have one input feature) let’s denote that as the x-axis. This can be considered the simplest example to show the dissimilarity between three data points A, B, and C. Let’s take an example where each data point contains only one input feature.
One means high similarity(the data objects are very similar). It is often expressed as a number between zero and one by conversion: zero means low similarity(the data objects are dissimilar). The similarity measure is usually expressed as a numerical value: It gets higher when the data samples are more alike. Another example is when we talk about dissimilar outliers compared to other data samples(e.g., anomaly detection). KNN), where the data objects are labeled based on the features’ similarity. All other data samples are grouped into different ones. Moreover, these terms are often used in clustering when similar data samples are grouped into one cluster. On the other hand, the dissimilarity measure is to tell how much the data objects are distinct. In data science, the similarity measure is a way of measuring how data samples are related or closed to each other. Illustrations and equations were generated using tools like Matplotlib, Tex, Scipy, Numpy and edited using GIMP. Quick note: Everything written and visualized has been created by the author unless it was specified. “There is no Royal Road to Geometry.” - Euclid To rank items as equivalent, overlap them.Various ML metrics. Heat distribution from high temperature to low temperature is a another example of this phenomenorn Part A Rank these systems in order of decreasing entropy. The universe started with low entropy (concentrated in the moment before the “big bang”) and the entropy has since been constantly increasing by distributing this energy. The universe has a constant amount of energy as stated in the first law of thermodynamics.
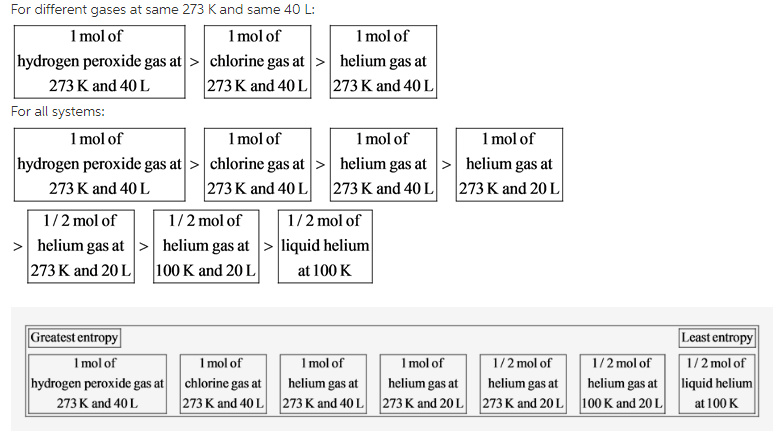
Another way of looking at entropy is that the universe is moving toward a broader distribution of energy. The number of molecules, the space available for the molecules, and the energy available to the molecules will impact the number of microstates. Duing rotational motion, molecules rotate or spin. During vibrational motion, atoms in a molecule move toward and away from one another. During translational motion, the entire molecule moves in one direction. Molecules may undergo three different types of motion: translational motion, vibrational motion, and rotational motion. The more microstates the system has, the greater its entropy Microstates depend on molecular motion. At the molecular level, entropy can be described in terms of the possible number of different arrangements of particle positions and energies, called microstates. Can you explain answers?Įntropy is the randomness of a system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
